Monitoring and evaluation
Contact
Introduction
Our research on monitoring and evaluation has identified some interesting findings, for example:
- Smart water meters can help businesses save water, particularly where they can identify leaks and continuous flows; anomalous peak days of use; and recurring high water use habits. These circumstances provide an informed platform for effective demand management strategies. (Using smart meters and data mining to inform demand management, Detection and interpretation of anomalous water use for non-residential customers, An incremental algorithm for discovering routine behaviours from smart meter data, Water use signature patterns for analyzing household consumption using medium resolution meter data)
- On-site monitoring and evaluation of groundwater conditions is critical to support better water sensitive urban design outcomes in high groundwater environments. (Guiding urban water management in areas that experience high seasonal groundwater: Expert Panel report)
- Water sensitive medium density housing designs have better water, urban heat and architectural and open space design characteristics and performance than conventional medium density development. (Infill typologies catalogue and Infill Performance Evaluation Framework)
- Constructed wetland water quality monitoring programs should consider that nitrogen processing in urban constructed wetlands varies temporarily (daily and seasonally), as well as spatially across wetlands. (Effectiveness of nitrogen removal using urban wetlands – summary report)
- A water quality monitoring program for untreated stormwater from 10 diverse urban catchments across Australia found the microbial quality of stormwater is highly variable. So, treatment is necessary to manage the health risks associated with stormwater harvesting schemes. (Microbial quality of untreated stormwater in Australian catchments: human health perspectives and Characterisation of chemical hazards in stormwater)
Performance of biological (vegetated) water treatment solutions
- Seasonal operation of dual-mode biofilters: The influence of plant species on stormwater and greywater treatment
- Dual-mode stormwater-greywater biofilters: The impact of alternating water sources on treatment performance
- Factors controlling dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in constructed stormwater urban wetlands
- Effectiveness of nitrogen removal using urban wetlands – summary report
- Microbial quality of untreated stormwater in Australian catchments: human health perspectives
- Temporal dynamics of stormwater nutrient attenuation of an urban constructed wetland experiencing summer low flows and macrophyte senescence
- Water Quality Dynamics of Urban Water Bodies during Flooding in Can Tho City, Vietnam
- Characterisation of chemical hazards in stormwater
- Validation framework for water-sensitive urban design treatment systems
- Surrogates for herbicide removal in stormwater biofilters
- Methodologies for Pre-Validation of Biofilters and Wetlands for Stormwater Treatment
- Determination of operational and challenge conditions for validation of stormwater biofilters and wetlands
- Sewage pollution in urban stormwater runoff as evident from the widespread presence of multiple microbial and chemical source tracking markers
- Evaluating Escherichia coli removal performance in stormwater biofilters: a preliminary modelling approach
- Predicting Between-Event Variability of Escherichia coli in Urban Storm Water
- Optimising nitrogen removal in existing stormwater biofilters: Benefits and tradeoffs of a retrofitted saturated zone
- Removal of Clostridium perfringens, Escherichia coli and F-RNA coliphages by stormwater biofilters
- Zinc-sulphate-heptahydrate coated activated carbon for microbe removal from stormwater
- The influence of design parameters on clogging of stormwater biofilters: A large-scale column study
- Modelling of stormwater biofilters under random hydrologic variability – a case study of a car park at Monash University, Victoria (Australia)
- Intra-event variability of Escherichia coli and total suspended solids in urban stormwater runoff
High groundwater
- Guiding urban water management in areas that experience high seasonal groundwater: Expert Panel report.
- The impact of urbanisation and stormwater management practices on water balances and nutrient pathways in areas of high groundwater: a review of recent literature
Water network performance
- Sensing-based leak quantification techniques in water distribution systems
- Detection and interpretation of anomalous water use for non-residential customers
- Sensor placement strategy for locating leaks using lean graphs
- An incremental algorithm for discovering routine behaviours from smart meter data
- A habit detection algorithm (HDA) for discovering recurrent patterns in smart meter time series
- Using smart meters and data mining to inform demand management
- Discovering routine behaviours in smart water meter data
- A habit discovery algorithm for mining temporal recurrence patterns in metered consumption data
- Water use signature patterns for analyzing household consumption using medium resolution meter data
- Making sense of smart metering data: A data mining approach for discovering water use patterns
- Discovering water use activities for smart metering
Wastewater system performance
- Influence of pressure main pumping frequency on sulfide formation rates in sanitary sewers
- A mechanistic model for anaerobic phototrophs in domestic wastewater applications: Photo-anaerobic model (PAnM)
- Modelling the long-term effect of wastewater compositions on maximum sulfide and methane production rates of sewer biofilm
- Low temperature treatment of domestic wastewater by purple phototrophic bacteria: Performance, activity, and community
- Domestic wastewater treatment with purple phototrophic bacteria using a novel continuous photo anaerobic membrane bioreactor
- Sulfide and methane production in sewer sediments: Field survey and model evaluation
- Stratified microbial structure and activity in sulfide- and methane-producing anaerobic sewer biofilms
- A kinetic model based on utilization of purple phototrophic bacteria for nutrient recovery
Evaluating the water performance of urban form
- Water sensitive outcomes for infill development: Infill performance evaluation framework
- Urban water metabolism information for planning water sensitive city-regions
- Understanding urban water performance at the city-region scale using an urban water metabolism evaluation framework
- Urban water metabolism indicators derived from a water mass balance – Bridging the gap between visions and performance assessment of urban water resource management
- Connecting land-use and water planning: Prospects for an urban water metabolism approach
- A metabolism perspective on alternative urban water servicing options using water mass balance
- Evaluation approaches for advancing urban water goals
- Urban metabolism for planning water sensitive cities
Research application
The CRCWSC’s research on monitoring and evaluation has been applied to:
- evaluate the performance of water sensitive infill development (Knutsford case study final report: water sensitive outcomes for infill development)
- quantify sediment export from the various stages of urban development at a site in Perth (Quantifying sediment export from an urban development site: Heron Park)
- assess the performance of a constructed wetland and make recommendations for improving wetland functions (Eric Singleton Constructed Wetland: Monitoring and assessment for optimal stormwater treatment performance)
- benchmark a large number of municipalities across Australia and internationally, including Moonee Valley (Moonee Valley Water Sensitive Cities Benchmarking and Water sensitive cities benchmarking and assessment: Mooney Valley City Council)
- show how real-time monitoring data and remote control of the on-lot water and energy systems can be applied to a residential development at Aquarevo (Aquarevo case study)
- consider the legal role of agencies to monitor and report on the health of wetlands (Legal duties for restoration of waterways and wetlands: a Western Australian analysis and case study)
- evaluate the influence of regulatory and risk allocation frameworks on decision making for an innovative stormwater harvesting and reuse project. (Kalkallo: a case study in technological innovation amidst complex regulation)
Tools and guidelines
We have developed industry guidance to assist with monitoring and evaluation, for example:
- the Water Sensitive Cities Index which is used to benchmark the progress of cities towards a water sensitive city state on the basis of 7 goals and 34 indicators (Water Sensitive Cities Index)
- A framework to guide the assessment and design of water sensitive infill development which can be used to compare different designs, generate metrics that feed into broader economic evaluations or building approval processes, identify targets and objectives for infill development, and predict the performance of new developments (Infill Performance Evaluation Framework)
- The RESTORE Tool which provides a framework to evaluate the importance, severity of stress and potential for repair of ecological components, to prioritise on-ground actions
- A guide for monitoring the performance of WSUD elements in areas with high groundwater which includes case studies demonstrating application
- A framework that describes how the CRCWSC will evaluate its own performance which can be easily adapted to assist in the evaluation of other programs (CRCWSC Evaluation and Learning Framework).
Infographics
Infographic 1
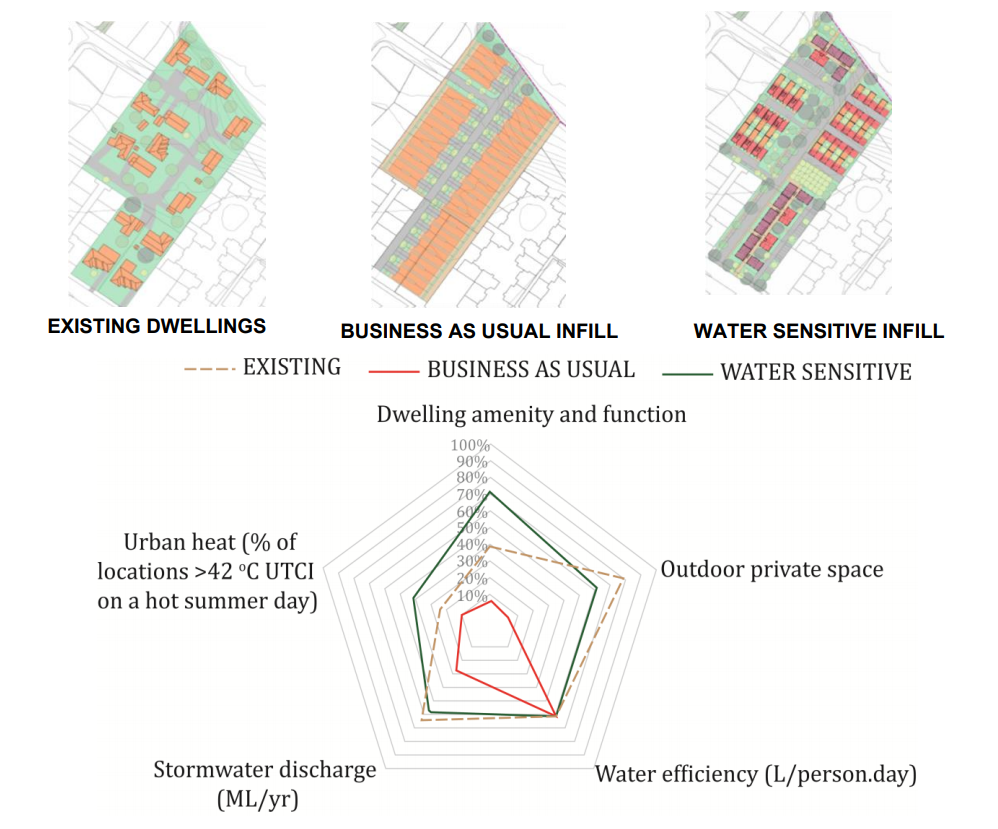
Performance monitoring requirements for higher risk WSUD elements in areas with high groundwater (Hunt et al., 2017. A guide for monitoring the performance of WSUD elements in areas with high groundwater. Melbourne, Australia: CRC for Water Sensitive Cities, p. 22.)
Infographic 2
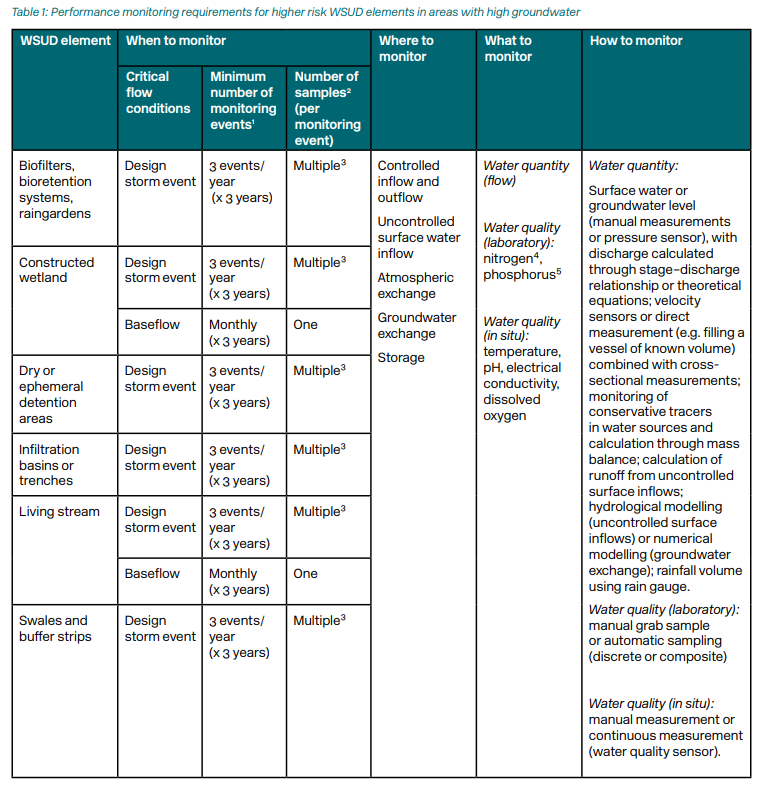
Conceptual model of perturbation of the urban water balance
(Ocampo CJ, 2018. The impact of urbanisation and stormwater management practices on water balances and nutrient pathways in areas of high groundwater: A review of recent literature. Melbourne, Australia: CRC for Water Sensitive Cities, p. 14.)
Infographic 3
Restore tool interface
(CRC for Water Sensitive Cities, 2018. Improving the ecological function of urban waterways: A compendium of factsheets. Melbourne, Australia: CRC for Water Sensitive Cities, p. 4.)

Infographic 4
Cause and effect framework (Renouf et al., 2020. Infill Performance Evaluation Framework. Melbourne, Australia: CRC for Water Sensitive Cities, p. 26.)
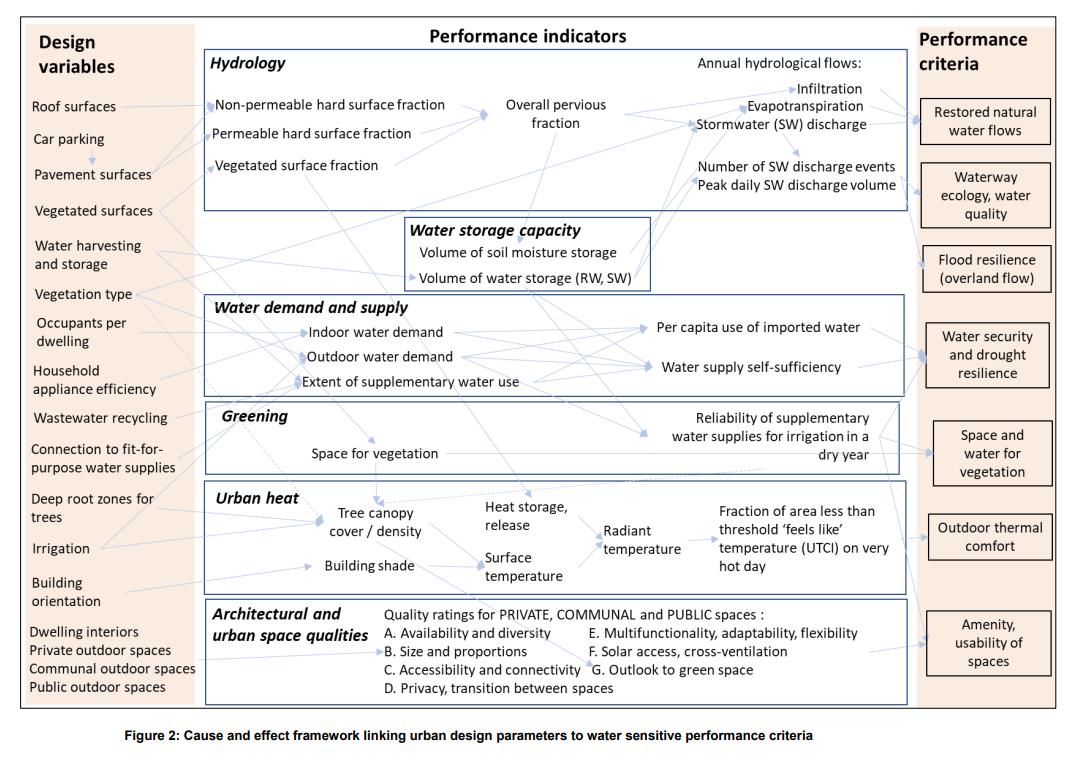
Infographic 5
Cause and effect framework (Renouf et al., 2020. Infill Performance Evaluation Framework. Melbourne, Australia: CRC for Water Sensitive Cities, p. 53.)