Current Water Sensitive Performance
Performance against the goals of a water sensitive city
Greater Perth was benchmarked using the Water Sensitive Cities Index in 2021, at a workshop attended by industry representatives.
The Water Sensitive Cities Index has also been used to benchmark municipalities within Greater Perth including Swan, Perth, Subiaco, Wanneroo, Mandurah, Canning, Cockburn, Manduring, Victoria Park, Vincent, Melville, Bayswater, Kwinanan, Cambridge, Belmont, Armadale, Bassendean and South Perth.
Greater Perth achieved its strongest result for the goal of Achieve equity of essential services (4.4/5.0). Areas for improvement included Improve productivity and resource efficiency (2.8/5/0), Ensure quality urban space (3.0/5.0) and Improve ecological health (3.0/5.0).
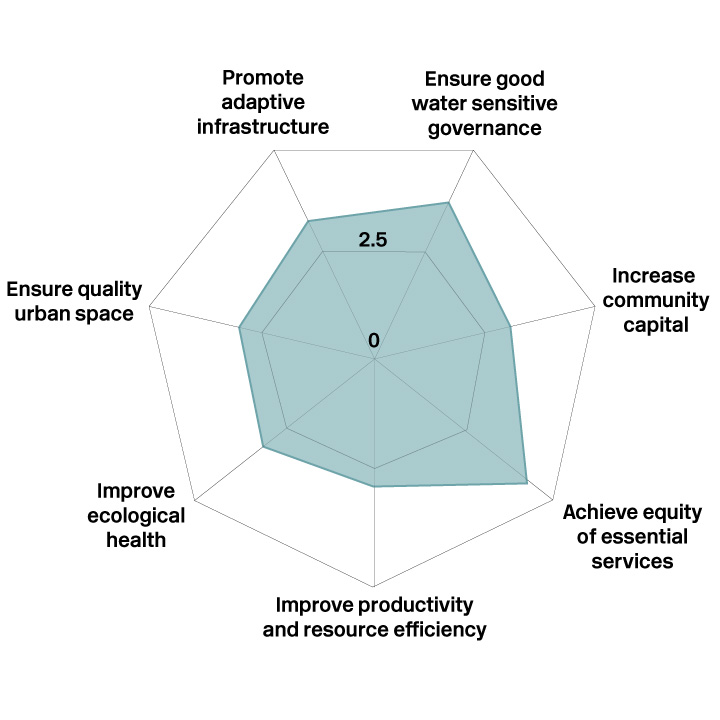
Achieving city–states
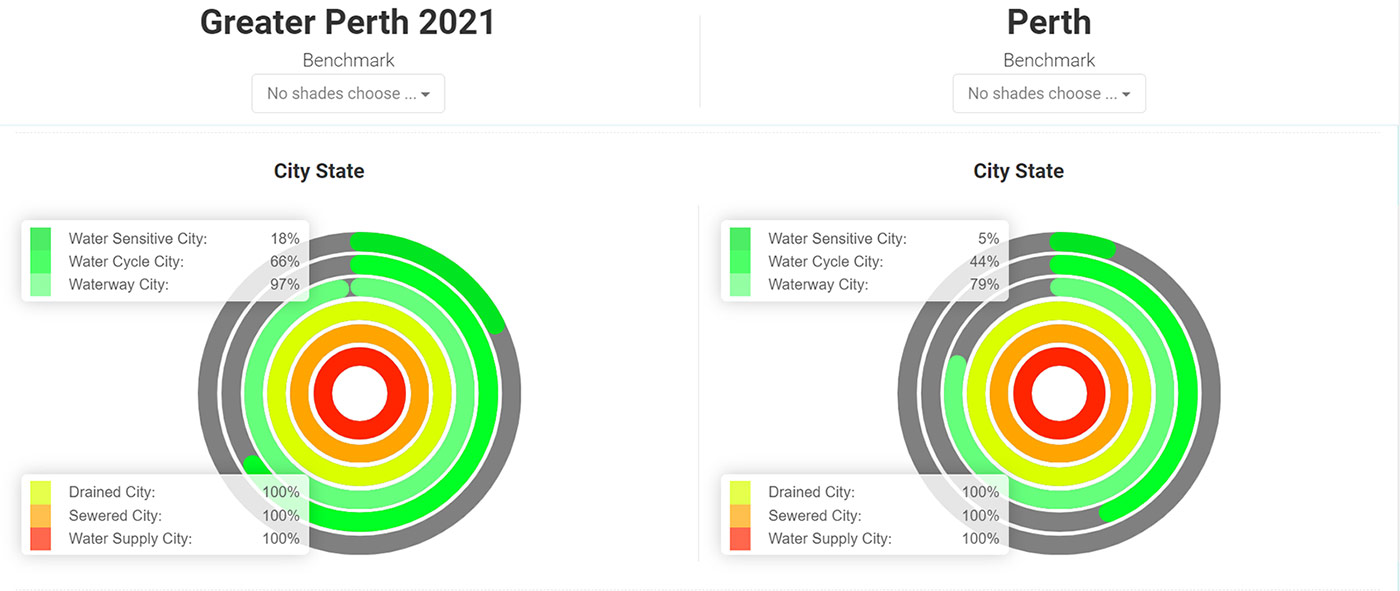
Greater Perth’s results against the 6 city–states highlights its strong performance is in providing basic services. It has equitable water supply and sanitation services that are safe, secure and affordable (100% Water Supply City and Sewered City) and the community is protected against floods (100% Drained City). Greater Perth also performs well in providing environmental sustainability services (97% Waterways City).
The most scope for improvement relates to using water to increase resilience (66% Water Cycle City) and liveability (18% Water Sensitive City).
Change strategy: how to become more water sensitive
- Vision and Transition Strategy for a Water Sensitive Greater Perth defines a vision of a water sensitive future for Perth and outlines the broad steps Perth can take to enable a transition towards this future.
- The 2065 vision for Greater Perth as a water sensitive city identifies four aspirational outcomes:
- Fostering stewardship of the system
- Protecting and enhancing the wellbeing of people and the environment
- Integrating and engaging with the built and natural landscape
- Sustaining the long term use of Perth’s resources
- Vision and Transition Strategy for a Water Sensitive Greater Perth – Implementation Plan 2019-2021 was developed by the Perth Water Sensitive Transition Network with assistance from the CRC for Water Sensitive Cities. It outlines actions and ideas to achieve Greater Perth’s water sensitive vision.
- Vision and Transition Strategy for a Water Sensitive Greater Perth - Implementation Plan 2022-2024 identifies priority actions for 2022–2024, proposing a framework for delivery, monitoring and review of Perth’s transition progress.
Research relevant to Perth
- The impact of water allocation reductions for horticultural licence holders in the Gnangara Groundwater System can be mitigated through changing cropping mixes and irrigation technology. (Regulatory renovation for managed aquifer recharge using alternative water resources: a Western Australian perspective)
- Subsurface drains in urban developments with shallow groundwater tables in the Swan Coastal Plain collect enough water to meet irrigation demands. (Urban subsurface drainage as an alternative water source in a drying climate)
- Achieving nitrogen and phosphorous reduction tasks in the Swan Canning catchment is estimated to cost $616 million. Introducing inventive based schemes and tighter regulation on fertiliser use would substantially reduce government costs of achieving the standards. (Cost-effective strategies to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus emissions in an urban river catchment)
- Restoring an urban drain to a wetland ecosystem increased the value of homes within 200 m of the restoration site by 4.7%. The project’s benefit to cost ratio was estimated to be 2.8 using a discount rate of 7%. (The value of restoring urban drains to living streams)
- Observational temperature data from 6 weather stations in Perth showed that during warm season heatwaves, the night time urban heat island effect in Perth is diminished (cooler than normal). Conversely, Melbourne and Adelaide experience and exacerbated UHI at night during heatwaves. (Is the urban heat island exacerbated during heatwaves in southern Australian cities?)
Hydrology
Urban subsurface drainage as an alternative water source in a drying climate
Hydrologic impact of urbanization with extensive stormwater infiltration
Will it rise or will it fall? Managing the complex effects of urbanization on base flow
Hydrological and nutrient modelling of the Swan Canning catchment-estuary system
Groundwater
Stormwater treatment
Assessment of options to improve amenity and performance of the Roselea Boulevard Compensation Basin
Microbial quality of untreated stormwater in Australian catchments: human health perspectives
Cost-effective strategies to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus emissions in an urban river catchment
Characterisation of chemical hazards in stormwater
Performance assessment of Wharf St Constructed Wetland 2009-2014
Performance of two urban stormwater biofilters in an area with seasonally high groundwater
Adaptation tipping points of a wetland under a drying climate
Stormwater biofiltration – the challenges of inorganic and organic nitrogen removal
E.coli removal in laboratory scale stormwater biofilters: Influence of vegetation and submerged zone
A multi-functional, multi-compartment constructed wetland to support urban waterway restoration
Pesticide occurrence and spatio-temporal variability in urban run-off across Australia
Waterways
Water supplies
The capitalized value of rainwater tanks in the property market of Perth report
The capitalized value of rainwater tanks in the property market of Perth, Australia
The most cost-effective ways to maintain public open space with less water: Perth case study
Detection and interpretation of anomalous water use for non-residential customers
Changing household water consumption practices after drought in three Australian cities
“A spirit of Bolshevism?” Perth’s water crisis of the 1920s
Lawnscaping Perth: Water supply, gardens, and scarcity, 1890-1925
The allure of climate and water independence: desalination projects in Perth and San Diego
Water sensitive cities and regions: tackling threats to water resources in metropolitan areas.
Other
The influence of statutory land use planning on water sensitive design practices
Is the urban heat island exacerbated during heatwaves in southern Australian cities?
Understanding social preferences for land use in wastewater treatment plant buffer zones
Legal duties for environmental water provisions in Western Australia
Advancing the adaptation of the water resource sector in highly urbanised regions across Australia
Connecting land use and water planning: Prospects for an urban water metabolism approach
Opportunity structures: understanding capacity for policy innovation
Transitioning to water sensitive cities: insights from six Australian cities
Becoming a water sensitive city: a comparative review of regulation in Australia
Results of a legislative stocktake for Western Australia
Performance assessment of the Anvil Way Compensation Basin living stream: 2004-2013
- Measuring the performance of water sensitive infill development at Knutsford examines how CRCWSC tools have been applied to the proposed Knutsford medium density infill development in Perth. In particular, the study demonstrates how the Infill Performance Evaluation Framework and the Benefit: Cost Analysis Tool have been applied to this site.
- Ideas for Queens Park Regional Open Space presents ideas to maximise the value delivered through efficient water use at the proposed open space. The ideas relate to:
- ensuring a sustainable water supply and water efficiency
- creating a waterwise landscape
- connecting bushland areas
- creating waterwise built form
- connecting with the city centre
- engaging the community.
- Ideas for the Subiaco Strategic Resource Precinct presents ideas to ensure the best use of land, water and other resources in the precinct which includes the Subiaco wastewater treatment plant and the associated buffer zone. The ideas relate to:
- developing a masterplan
- developing a water management strategy
- reducing heat wave temperature across the precinct and minimising net energy use
- connecting and enhancing green infrastructure
- developing an innovation hub.
- Water Sensitive Outcomes for Infill Development: Knutsford Case Study Final Report documents the application of the Infill Performance Evaluation Framework to an infill development in the City of Fremantle. The case study demonstrates how coordinating architectural and water services design can mitigate hydrological changes, and water demands, as well as improve the overall liveability of a development.
- Brabham Action Learning Partnership: Case report summarises context analysis and considers implementation pathways for a proposed non-potable water supply system at a development in the City of Swan. A companion report, Enabling water sensitive urban development: planning and governance opportunities for Perth outlines the planning and governance ideas for the system.
Ideas for the Subiaco Strategic Resource Precinct
Revitalising Canning City Centre: A water sensitive perspective
Water Sensitive Outcomes for Infill Development: Knutsford Case Study Final Report
Quantifying sediment export from an urban development site: Heron Park
Enabling water sensitive urban development: planning and governance opportunities for Perth
Brabham Action Learning Partnership: Case report
Bannister Creek living stream case study
Kalamunda managed aquifer recharge case study
- Guiding urban water management in areas that experience high seasonal groundwater: Expert Panel report synthesises the panel’s understanding of best practice methodologies for assessing and managing groundwater. Key guidance relates to using a risk-based framework, adopting consistent and coherent modelling, demonstrating robust and resilient design and construction approaches, and developing and using technical assessment tools.
- Riparian design guidelines to inform the ecological repair of urban waterways identify how urbanisation impacts 10 ecological processes performed by riparian zones and provides a management framework for prioritising actions to mitigate these impacts. The guidelines refer to many examples in the Perth region.
- Vegetation guidelines for stormwater biofilters in the south-west of Western Australia describe biofilters and how vegetation impacts infiltration rates, evapotranspiration and nitrogen removal. Plant lists are provided for plants that have been found to be effective at removing nitrogen and plants that are likely to be suited to biofilters.
- A guide for monitoring the performance of WSUD elements in areas with high groundwater focuses on quantitative monitoring of the nutrient removal performance of WSUD assets and presents an overview of monitoring and analysis techniques in areas where high groundwater may influence asset performance.
Riparian design guidelines to inform the ecological repair of urban waterways
Vegetation guidelines for stormwater biofilters in the south-west of Western Australia
A guide for monitoring the performance of WSUD elements in areas with high groundwater
BCA Tool (INFFEWS) Webinar – insights from industry applications
Non-market valuation of recycled water: Subiaco Strategic Resource Precinct case study fact sheet
Assessment of non-market benefits of WSUD for a residential development: a case study fact sheet
Mind the gap–what we don’t know about urban areas with high groundwater fact sheet
The most cost-effective ways to maintain public open space with less water fact sheet
Water and the Australian city: lessons from history fact sheet
Projects to mainstream water sensitive practice
Mainstreaming projects help water sensitive approaches become standard practice, supported by strong
community demand, robust science, technical capability, sufficient funding and supportive governance.





